Watch and decode Cisco Discovery Protocol Packetes.
- CDP Monitor-Script
- Real-Life Example
- Run this script:
- Open another CMD-Window to spin up a new CSR1000V-Router:
- Go back to the „python“-Screen and wait:
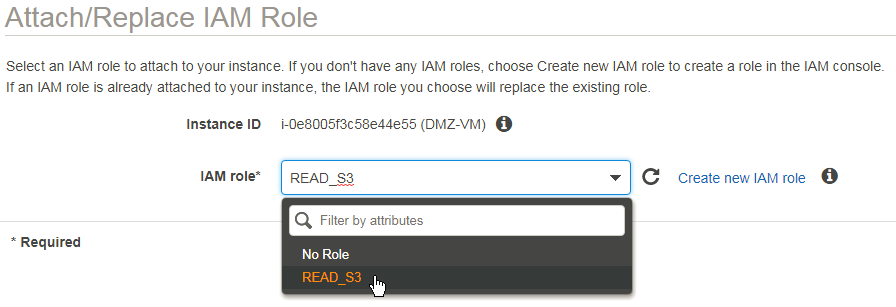
- Hostname
- Interface set to „ip address dhcp“
- CDP enabled
Inspired by the Scapy ARP-Monitor i created an CDP-Monitor displaying hostname and an optional Management-IP-Address.
#! /usr/bin/env python
from scapy.all import *
load_contrib("cdp")
def cdp_monitor_callback(pkt):
ip = "0.0.0.0"
if (CDPMsgDeviceID in pkt):
device=pkt["CDPMsgDeviceID"].val.decode()
hostname=device.split(".")[0]
if (CDPAddrRecordIPv4 in pkt):
ip=pkt["CDPAddrRecordIPv4"].addr
return "Device: {0} IP: {1}".format(hostname,ip)
interface="VirtualBox Host-Only Ethernet Adapter"
capturefilter="ether dst 01:00:0c:cc:cc:cc"
# run it for max. 99 Packets
p=sniff(prn=cdp_monitor_callback, iface=interface, count=99, filter=capturefilter, store=0)
C:\RH>python
Python 3.7.0 (v3.7.0:1bf9cc5093, Jun 27 2018, 04:59:51) [MSC v.1914 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> #! /usr/bin/env python
... from scapy.all import *
>>> load_contrib("cdp")
>>>
>>> def cdp_monitor_callback(pkt):
... ip = "0.0.0.0"
... if (CDPMsgDeviceID in pkt):
... device=pkt["CDPMsgDeviceID"].val.decode()
... hostname=device.split(".")[0]
... if (CDPAddrRecordIPv4 in pkt):
... ip=pkt["CDPAddrRecordIPv4"].addr
... return "Device: {0} IP: {1}".format(hostname,ip)
...
>>> interface="VirtualBox Host-Only Ethernet Adapter"
>>> capturefilter="ether dst 01:00:0c:cc:cc:cc"
>>>
>>> # run it for max. 99 Packets
... p=sniff(prn=cdp_monitor_callback, iface=interface, count=99, filter=capturefilter, store=0)
C:\RH\work\entwicklung\csr1000v-provision-in-virtualbox>CSR1000v-Virtual-Box.cmd Enter CSR1000v Hostname:CSR-CDPTEST-A Virtual machine 'CSR-CDPTEST-A' is created and registered. UUID: eaa931bd-9db4-4a78-b263-754d4bb300a0 Settings file: 'c:\RH\LAB\VM\CSR-CDPTEST-A\CSR-CDPTEST-A.vbox' Creating ISO image at c:\RH\LAB\VM\CSR-CDPTEST-A\config.iso, 1 Files, Size: 8,00 KB 100% 0%...10%...20%...30%...40%...50%...60%...70%...80%...90%...100% Medium created. UUID: 3019216e-2e61-435a-95f2-3d26312c3ed9 Waiting for VM "CSR-CDPTEST-A" to power on... VM "CSR-CDPTEST-A" has been successfully started.
>>> # run it for max. 99 Packets ... p=sniff(prn=cdp_monitor_callback, iface=interface, count=99, filter=capturefilter, store=0) Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 0.0.0.0 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 0.0.0.0 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 0.0.0.0 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 0.0.0.0 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 0.0.0.0 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 10.0.2.15 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 10.0.2.15 Device: CSR-CDPTEST-A IP: 10.0.2.15
It works, the IOS-XE CSR1000V-Router is installed and it got it’s baseline-config applied:
takes some time, but these first CDP-Packets captured were not sent in 60s interval, so don’t be scared 😉