about:config
browser.download.alwaysOpenPanel
switch to „false“
networking, computing, virtualization, automation
about:config
browser.download.alwaysOpenPanel
switch to „false“
everybody knows about IPv6 „2001:db8“ – but about the IPv4 pendants?
The blocks
are provided for use in documentation.
The „refreshenv“-CMD/Powershell-Command updates all Environment-Variables e.g. after installing a new software package.
C:\WINDOWS\system32>refreshenv
Refreshing environment variables from registry for cmd.exe. Please wait...Finished..
Both Protocols are absolutely useless for all common use-cases, but enabled – just „providing“ potential security issues.
Disable like this:
netsh interface isatap set state disabled
netsh interface teredo set state disabled
I prefer accessing VMs using SSH or RDP directly. Sometimes, the IP-Address of the VM isn’t reachable, or protocols for remoteaccess need to be disabled for security reasons.
In these cases, if an IP-connection to the ESXi-Server is available this could be an option to use the ESXi hypervisor as VNC-Server to provide access to VM keyboard, video, mouse…
Three VM advanced Configuration Parameters need to be set:
RemoteDisplay.vnc.enabled = TRUE
RemoteDisplay.vnc.port = <TCP-Port>
RemoteDisplay.vnc.password = <Passwort>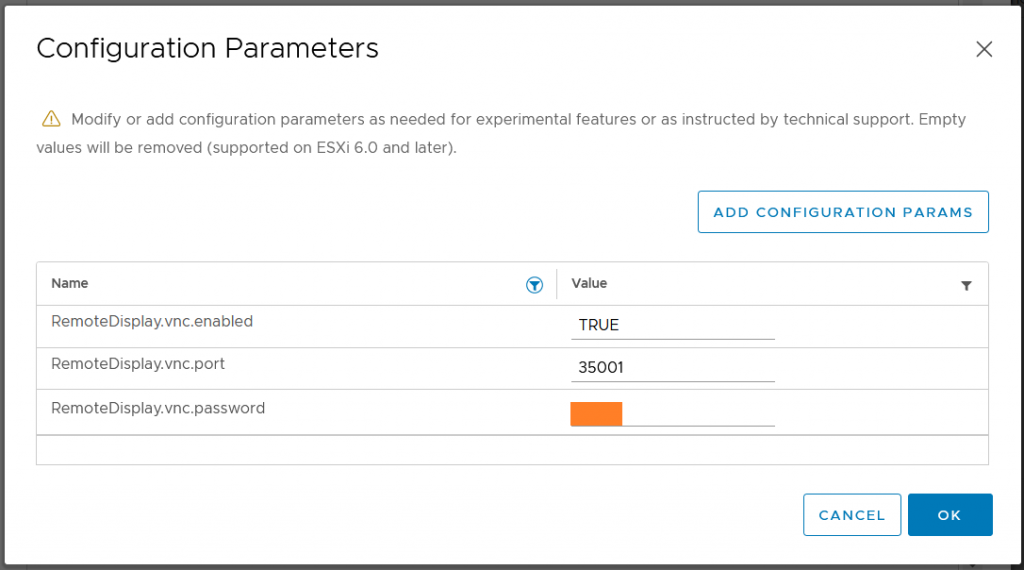
No „do you really want to leave“ windows any more, how nice is that!?
https://romanisthere.github.io
Don’t delete the content of „c:\windows\ccmcache\“ manually with the File-Explorer:
You need „local Administrator“ access to your computer.
Let SCCM to cleanup it’s cache for you:
1) open the „Control Panel“
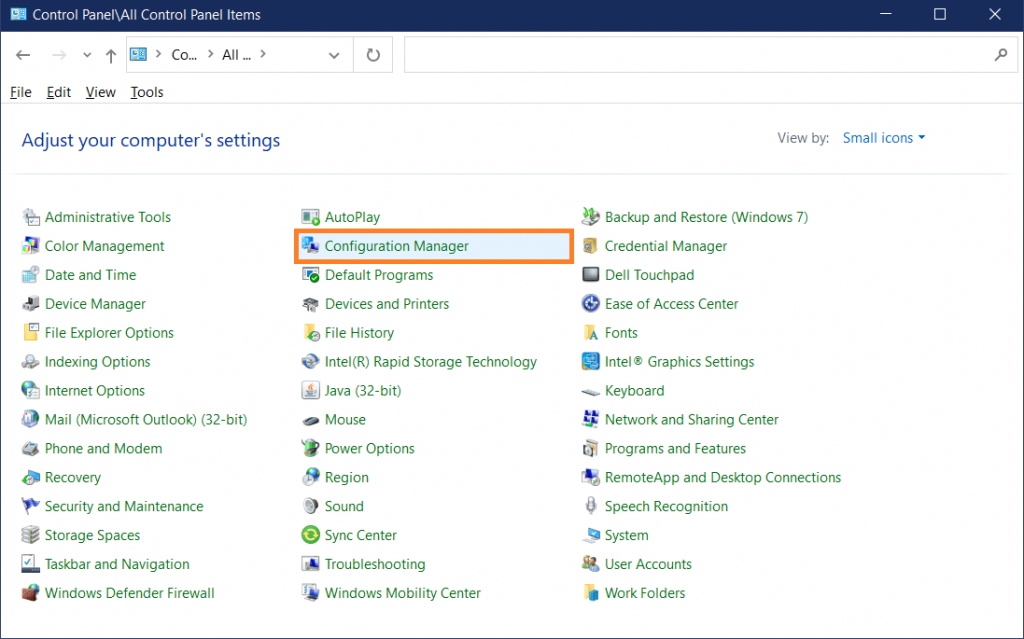
2) select „Configuration Manager“
3) go to „Cache“-Tab
4) click „Delete Files“
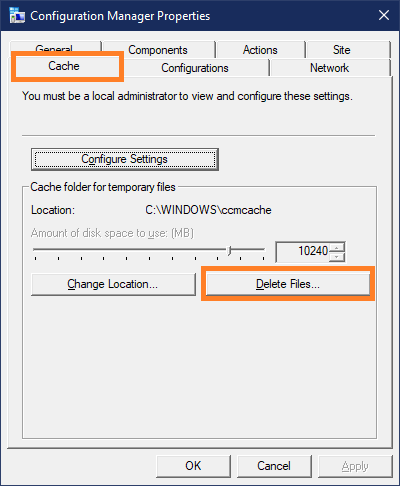
Wait a second and the CCM-Cache is empty.
c:\Windows\ccmcache>dir
Volume in drive C is Windows
Volume Serial Number is 5Q4C-0K08
Directory of c:\Windows\ccmcache
23.09.2021 19:10 <DIR> .
23.09.2021 19:10 <DIR> ..
0 File(s) 0 bytes
2 Dir(s) 11.164.721.152 bytes free
While the „old“ SCAv1 built a virtual fence around all virtual processors („Intra VM Security Boundary“), SCAv2 lets processors of one virtual machine (VM) to run within a „common fence“ („Inter VM Security Boundary“) which balances security and performance for most workloads.
See https://www.vmware.com/content/dam/digitalmarketing/vmware/en/pdf/techpaper/performance/scheduler-options-vsphere67u2-perf.pdf for performance analysis.
esxcli system settings kernel set -s hyperthreadingMitigation -v TRUE
esxcli system settings kernel set -s hyperthreadingMitigationIntraVM -v FALSE
esxcli system settings kernel list -o hyperthreadingMitigation
esxcli system settings kernel list -o hyperthreadingMitigationIntraVM
[root@esx:~] esxcli system settings kernel list -o hyperthreadingMitigation
Name Type Configured Runtime Default Description
------------------------ ---- ---------- ------- ------- ----------------------------------------------------------------
hyperthreadingMitigation Bool TRUE TRUE FALSE Restrict the simultaneous use of logical processors from the
same hyperthreaded core as necessary to mitigate a security
vulnerability.
[root@esx:~] esxcli system settings kernel list -o hyperthreadingMitigationIntraVM
Name Type Configured Runtime Default Description
------------------------------- ---- ---------- ------- ------- ---------------------------------------------------------
hyperthreadingMitigationIntraVM Bool FALSE FALSE TRUE Restrict the simultaneous use of logical processors from
the same hyperthreaded core as necessary to mitigate a
security vulnerability within a single VM.
esxcli system settings kernel set -s hyperthreadingMitigation -v TRUE
esxcli system settings kernel set -s hyperthreadingMitigationIntraVM -v TRUE
Comments are greyed out by default, nobody should read them 😉 I don’t want to think about the comment-quality of the Atom-Sourcecode, just kidding 😉
To change the comment-colour to a fresh and visible green:
c:\>notepad c:\Users\<username>\.atom\styles.lessatom-text-editor::shadow { .punctuation.comment, .comment, .link.hyperlink { color: #88ff88; } }
My WIFI is bound to my Internet-Router and it is seperated from my home-office by an routed stateful-firewall. Some WIFI devices (for example my printer) need access to this home-office ip-range.
The DHCP-Service of my pi-hole server usually offers just dhcp-option #3 – the default-gateway.
The pi-hole Web-GUI doesn’t allow to specify additional dhcp-options, so first disable offering the default-gateway-option:

which is not allowed (my opinion: a bug since this is no feature)
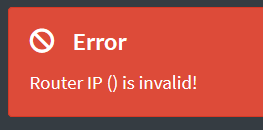
Stop here and use another dhcp-service?
Fortunately RFC3442 („The Classless Static Route Option for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) version 4“) https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/html/rfc3442 states:
If the DHCP server returns both a Classless Static Routes option and a Router option, the DHCP client MUST ignore the Router option.
So this can stay enabled, it’ll be ignored – and, just for the case an old DHCP-Client doesn’t implement the Classless Static-Routes Option it’ll ignore it and can use the Default-Gateway-option.
adminname@pi-hole-server:/etc/dnsmasq.d $ ls -l
total 16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1524 May 22 13:16 01-pihole.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 490 May 22 13:16 02-pihole-dhcp.conf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 143 Dec 8 14:04 04-pihole-static-dhcp.conf
adminname@pi-hole-server:cat 01-pihole.conf
# Pi-hole: A black hole for Internet advertisements
# (c) 2017 Pi-hole, LLC (https://pi-hole.net)
# Network-wide ad blocking via your own hardware.
#
# Dnsmasq config for Pi-hole's FTLDNS
#
# This file is copyright under the latest version of the EUPL.
# Please see LICENSE file for your rights under this license.
###############################################################################
# FILE AUTOMATICALLY POPULATED BY PI-HOLE INSTALL/UPDATE PROCEDURE. #
# ANY CHANGES MADE TO THIS FILE AFTER INSTALL WILL BE LOST ON THE NEXT UPDATE #
# #
# IF YOU WISH TO CHANGE THE UPSTREAM SERVERS, CHANGE THEM IN: #
# /etc/pihole/setupVars.conf #
# #
# ANY OTHER CHANGES SHOULD BE MADE IN A SEPARATE CONFIG FILE #
# WITHIN /etc/dnsmasq.d/yourname.conf #
###############################################################################
addn-hosts=/etc/pihole/local.list
...
So lets add „/etc/dnsmasq.d/yourname.conf“:
I’d like to create
sudo echo "
dhcp-option=option:classless-static-route,0.0.0.0/0,172.16.1.1,10.0.0.0/8,172.16.1.2,172.16.0.0/12,172.16.1.2,192.168.0.0/16,172.16.1.2" > 99-user-settings.conf
sudo service pihole-FTL reload
Horrible – Windows 10 states a „default-gateway“ to be set 🙁
C:\Users\user>ipconfig /renew "WLAN"
Windows-IP-Konfiguration
Drahtlos-LAN-Adapter WLAN:
Verbindungsspezifisches DNS-Suffix: prod.local
IPv4-Adresse . . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.1.14
Subnetzmaske . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Standardgateway . . . . . . . . . : 172.16.1.1
But the ip routing-table is fine: even Windows 10 implements RFC3442:
C:\Users\user>route print
===========================================================================
IPv4-Routentabelle
===========================================================================
Aktive Routen:
Netzwerkziel Netzwerkmaske Gateway Schnittstelle Metrik
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1 172.16.1.14 35
10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.14 36
127.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Auf Verbindung 127.0.0.1 331
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 Auf Verbindung 127.0.0.1 331
172.16.0.0 255.240.0.0 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.14 36
192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 172.16.1.2 172.16.1.14 36
172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Auf Verbindung 172.16.1.14 291
255.255.255.255 255.255.255.255 Auf Verbindung 172.16.1.14 291
===========================================================================
Forget it, Google seems to not priotize fixing basic low-level IP-Stack issues, it’s embarrassing: https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/36920068